Anthony Gary - July 01 2024
The Spectrum of Plant Lights: Understanding the Key to Optimal Growth
In the world of gardening and horticulture, lighting plays a crucial role in the growth and health of plants. While natural sunlight is the ideal source of light for plant growth, indoor gardening and certain agricultural practices often require artificial lighting. Understanding the spectrum of plant lights is essential for providing the optimal conditions for photosynthesis, flowering, and fruiting. This article delves into the science behind plant light spectra and how different types of Grow lights cater to the needs of various plants.
The Science of Light and Plant Growth
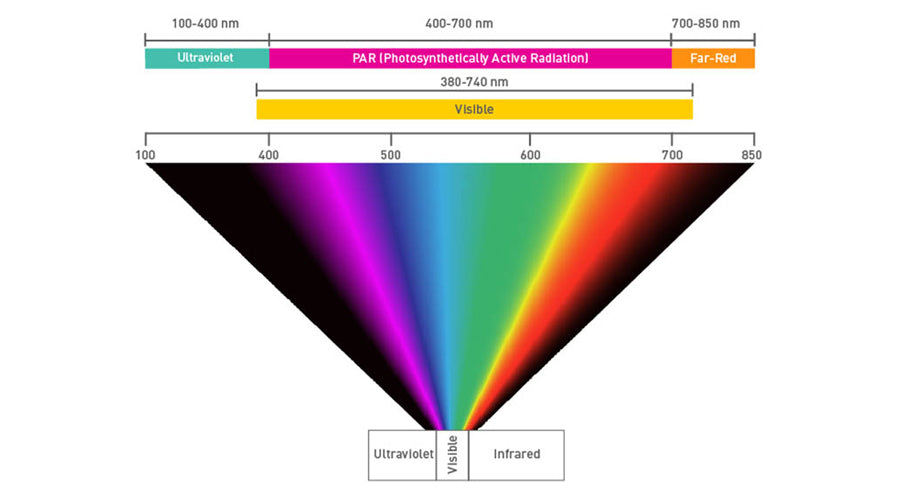
Light is composed of electromagnetic waves, and the visible spectrum ranges from approximately 400 to 700 nanometers (nm). This range of light is divided into different colors, each corresponding to a specific wavelength:
Violet: 380-450 nm
Blue: 450-495 nm
Green: 495-570 nm
Yellow: 570-590 nm
Orange: 590-620 nm
Red: 620-750 nm
Plants use light primarily for photosynthesis, the process by which they convert light energy into chemical energy. Chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis, absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and red regions of the spectrum. However, different stages of a plant’s life cycle may require different light spectra.
Blue Light (450-495 nm)
Blue light is crucial for the vegetative stage of plant growth. It promotes strong root development, sturdy stems, and healthy leaves. Blue light helps regulate plant growth by influencing the opening of stomata (tiny pores on the leaf surface) and enhancing photosynthetic activity. In indoor gardening, blue light is often used to prevent plants from becoming leggy and weak.
Blue Light (450-495 nm)
Red light is essential for the reproductive stage of plant growth, including flowering and fruiting. It influences the length of the night period, triggering flowering in many plants. Red light also plays a role in seed germination and root development. Combining red and blue light is a common practice to ensure a balance between vegetative growth and flowering.
Full Spectrum Light
Full spectrum lights mimic natural sunlight by providing a balanced range of wavelengths across the visible spectrum. These lights are designed to support all stages of plant growth, from seedling to flowering. Full spectrum lights are particularly useful in environments where natural light is limited, such as greenhouses and indoor gardens.

Full spectrum
Supplemental Spectra: Far-Red and UV Light
Far-Red Light (700-800 nm): Far-red light can influence plant morphology and flowering. It can extend the photoperiod, encouraging plants to flower sooner or alter their growth patterns. Far-red light is often used in combination with red light to enhance flowering in certain plants.
UV Light (100-400 nm): Ultraviolet (UV) light, particularly UV-A (320-400 nm) and UV-B (280-320 nm), can affect plant growth and defense mechanisms. While excessive UV light can be harmful, small doses can enhance the production of certain pigments, increase disease resistance, and improve the overall quality of plants.
Types of Artificial Plant Lights
Light Emitting Diode (LED) Lights: LEDs are highly energy-efficient and can be tailored to emit specific wavelengths. Full spectrum LED grow lights are popular for their versatility and ability to support all stages of plant growth.
Fluorescent Lights: These lights are cost-effective and widely used for seedlings and low-light plants. They emit a balanced spectrum suitable for vegetative growth but are less effective for flowering plants.
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Lights: HID lights, including Metal Halide (MH) and High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) lights, are powerful and efficient. MH lights emit more blue light, making them ideal for vegetative growth, while HPS lights emit more red light, promoting flowering and fruiting.
Incandescent Lights: These lights are not recommended for plant growth as they emit more heat than light and have a poor light spectrum for photosynthesis.
Choosing the Right Light Spectrum
Selecting the appropriate light spectrum depends on the type of plants being grown and their specific growth stages. Here are a few tips:
- For seedlings and vegetative growth, prioritize blue light or full spectrum lights with a higher blue light ratio.
- For flowering and fruiting, incorporate red light or full spectrum lights with a higher red light ratio.
- Consider full spectrum LED lights for a versatile solution that supports all stages of plant growth.